iPHACTORY
This is a project funded by the DFG in collaboration with Anna Matuszyńska (Heinrich Heine University, Düsseldorf), who is performing metabolic modelling. Using a combination of transcriptomics and metabolomics we were able to show previously that glandular trichomes of tomato, although they are photosynthetic, import carbon in the form of sucrose (Balcke et al., 2017). Photosynthesis is used to provide chemical energy and reducing equivalents to fuel the biosynthesis of terpenoids. In addition, we hypothesize that CO2 generated by the metabolic pathways is recycled by ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase (RubisCo) either as part of a full Calvin Bassham Benson (CBB) cycle or of a bypass involving the oxidative pentose phosphate pathway. To test these hypotheses we are generating tomato lines where specific genes are either knocked-out, down- or up-regulated. Specific targets include a trichome specific isoform of the small subunit of RubisCo, of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK), or ATP-citrate lyase. These will be analysed using metabolomics approaches, thus providing data to refine the model in an iterative fashion.
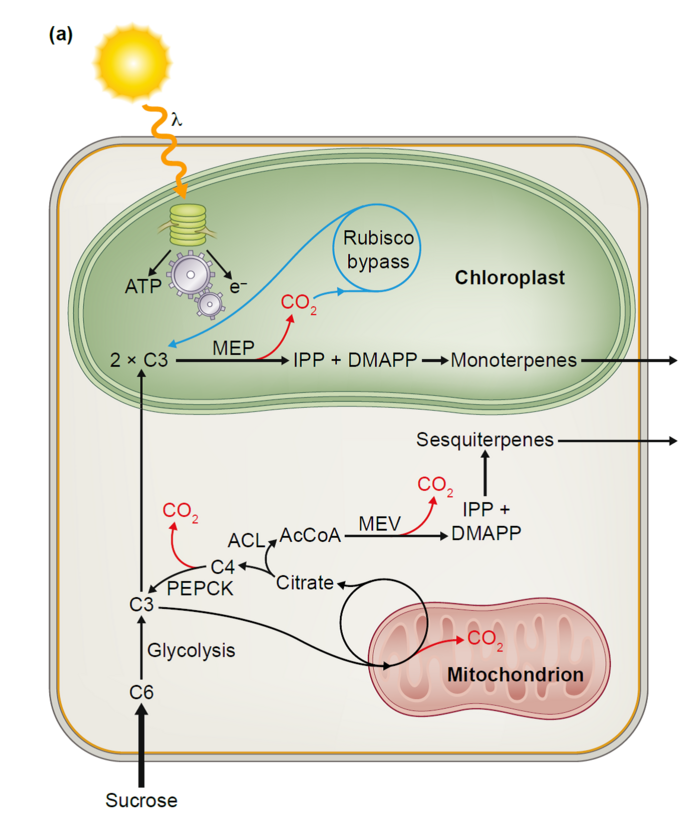
A simplified model of photosynthetic glandular trichomes in tomato (from Schuurink & Tissier, 2019). The main products are monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes, derived from the plastidic methyl-erythritol phosphate (MEP) and the mevalonate (MEV) pathways, respectively. Despite being photosynthetic, trichomes import sucrose form the leaf, which is then metabolized to C3 products via glycolysis. The supply of acetyl-CoA (AcCoA) in the cytosol is secured through the citrate shuttle with the mitochondria, because AcCoA cannot cross the mitochondrial membrane. The first step of the tricarboxylic acid cycle in the mitochondria produces citrate, which is exported to the cytosol, where it is split into oxalate (C4) and AcCoA by ATP-citrate lyase (ACL). The C4 dicarboxylic acids can then be either converted back to a C3 (in this case phosphoenol pyruvate) through the activity of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) or imported back to the mitochondria. C3 triose-phosphates can also be transported to the chloroplasts where they will be used as precursors for the plastidial isoprenoid precursor pathway (MEP) pathway. In the chloroplast, light photosynthesis is active and supplies chemical energy (ATP) and reducing power that are needed to fuel the metabolic reactions. In addition, it is suspected that the large quantities of CO2 released by the various reactions taking place (highlighted in red) are refixed via the activity of ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase (RubisCo) in the so-called RubisCo bypass.
Members involved
- Alejandro Brand (PhD Student)
- Gerd Balcke (IPB scientist)
- Anja Henning (IPB technician)
- Anna Matuszyńska (HHU)
This page was last modified on 27 Jan 2025 27 Jan 2025 27 Jan 2025 .

